In recent years, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending has emerged as a disruptive force in India’s financial sector, offering an alternative to traditional banking. P2P lending platforms allow individuals to lend and borrow money directly from each other, bypassing conventional banks. These platforms have gained traction as they address critical gaps in credit accessibility, especially for underserved individuals and small businesses. With the rise of digital finance, regulatory support, and growing demand for flexible lending options, the P2P lending industry in India is on a significant growth trajectory.

What is Peer-to-Peer Lending?
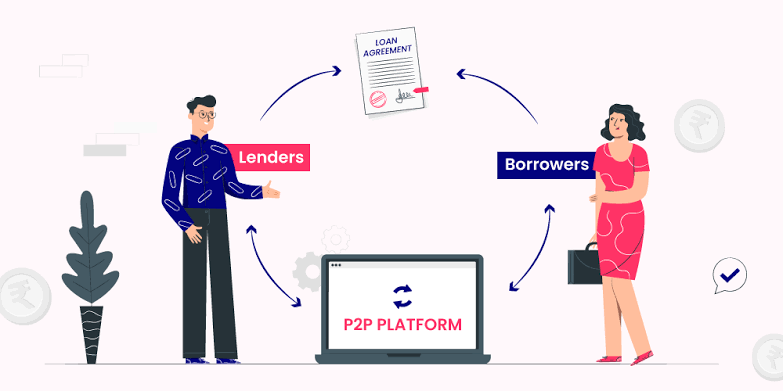
Peer-to-peer lending is a decentralized form of lending where borrowers can access funds directly from individual lenders without involving banks or financial institutions. Using an online platform, a borrower posts their loan requirements, and individual lenders can choose to fund these loans in exchange for attractive interest rates. The P2P platform facilitates the transaction, verifies borrower credentials, and ensures secure repayments, earning a fee for the services provided.
In India, P2P lending appeals primarily to individuals and small businesses that may find it challenging to secure credit through traditional banks due to strict eligibility requirements or a lack of formal credit history.
Rise of P2P Lending in India
The rapid growth of P2P lending in India is driven by various factors:
- Limited Access to Traditional Credit: Many Indians, especially small business owners and first-time borrowers, find it difficult to access formal loans due to stringent requirements and lengthy approval processes. P2P lending provides these individuals with an alternative credit source.
- Attractive Returns for Lenders: For lenders, P2P platforms offer higher interest rates compared to traditional savings accounts or fixed deposits. This makes P2P lending an appealing option for those seeking better returns on their investments, especially in a low-interest-rate environment.
- Digital and Mobile Penetration: With the rise of smartphone usage and digital banking, India’s financial ecosystem is becoming increasingly tech-driven. P2P lending platforms have capitalized on this trend, offering seamless online processes, easy accessibility, and user-friendly interfaces.
- Regulatory Support: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recognized the potential of P2P lending and introduced regulations in 2017, designating P2P platforms as non-banking financial companies (NBFC-P2P). This regulatory framework has provided credibility to the sector, ensuring transparency and reducing risks for lenders and borrowers.
How P2P Lending Works in India

The functioning of P2P lending platforms in India is straightforward. A borrower signs up on the platform, providing essential details, including income, credit score, and loan requirements. The platform conducts due diligence, verifies the borrower’s information, and assesses the risk involved. Once verified, the borrower’s profile is listed on the platform, where potential lenders can review the details and choose to fund the loan.
Lenders can either fund a single loan or diversify their investments across multiple loans to minimize risks. The platform typically handles disbursements, repayments, and collections. Lenders earn interest based on the risk level associated with the loan and the repayment period, while platforms charge a nominal fee to cover operational expenses.
Advantages of P2P Lending
P2P lending brings multiple benefits to the financial ecosystem:
- For Borrowers: P2P lending platforms offer a more flexible and accessible route to credit, especially for those with limited banking options. Borrowers often find P2P lending to be quicker, with shorter approval times and fewer documentation requirements.
- For Lenders: Investors enjoy attractive returns on their investments. P2P platforms provide greater control over investment decisions, allowing lenders to diversify their portfolios and manage risk more effectively.
- For the Economy: P2P lending contributes to financial inclusion by extending credit to underserved sectors, such as small businesses, entrepreneurs, and low-income individuals. This helps stimulate economic growth and supports the country’s digital financial goals.
Challenges Facing P2P Lending Platforms
Despite its growth, the P2P lending industry faces several challenges:
- Credit Risk: Lending without collateral increases the risk of default. Many P2P lending platforms have implemented robust risk assessment algorithms and scoring systems to mitigate this, but credit risk remains a significant concern, especially as P2P lenders often cater to high-risk borrowers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Although RBI regulations have brought legitimacy to the sector, compliance with these guidelines can be challenging for small and new platforms. Meeting capital requirements, maintaining proper records, and following due diligence protocols can strain platform resources.
- Limited Awareness: P2P lending is relatively new to the Indian market, and many potential borrowers and lenders remain unaware of how it works. Increasing public awareness and building trust are essential for the sustained growth of P2P lending.
- Competition from Traditional Banks and NBFCs: As banks and NBFCs adapt to digital transformation, they may introduce competing loan products, posing a challenge to P2P platforms. These established players have more resources and credibility, which could impact the market share of P2P lenders.
The Future of P2P Lending in India
As the Indian financial landscape continues to evolve, the future of P2P lending looks promising. The industry is expected to grow significantly, driven by the demand for alternative credit sources, rising digital adoption, and a supportive regulatory framework. In the coming years, we can expect to see several trends in the P2P lending space:
- Increased Use of AI and Big Data: P2P platforms are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and big data analytics for credit risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized loan offerings. These technologies can help platforms improve risk management and deliver a better experience for borrowers and lenders alike.
- Expansion into Rural and Semi-Urban Areas: To achieve true financial inclusion, P2P lending platforms will likely expand their reach to rural and semi-urban regions where access to credit remains limited. By catering to these underserved markets, P2P platforms can play a significant role in bridging the financial inclusion gap.
- Collaborations with Traditional Financial Institutions: To enhance their credibility and reach, some P2P platforms are exploring partnerships with traditional banks and NBFCs. These collaborations could create a hybrid model where traditional institutions support risk assessment and lending processes while the P2P platform manages borrower-lender interactions.
Conclusion: P2P Lending as a Game-Changer
P2P lending is revolutionizing the Indian lending landscape by democratizing access to credit and empowering both borrowers and lenders. As a fast-growing sector, it has the potential to reshape financial services in India, contributing to greater financial inclusion and providing more people with the financial tools needed to succeed. While challenges remain, the industry’s adaptability, technological advancements, and regulatory backing make it well-positioned for long-term growth.
For investors, P2P lending offers a unique opportunity to earn attractive returns while diversifying their portfolios. For borrowers, it provides a viable alternative to traditional loans, especially in an era where banks have become increasingly selective about lending. As the P2P sector matures, it will play an essential role in India’s journey toward a more inclusive, digitally-driven financial ecosystem.
