In recent years, India has made significant strides toward promoting sustainable finance, especially through its push for green bonds. With growing global awareness about climate change and the need for environmentally responsible investments, India’s efforts in the green finance space are both timely and essential. This move not only aligns with India’s environmental commitments, such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement, but also paves the way for a greener, more resilient economic future.
What are Green Bonds?
Green bonds are debt instruments used specifically to fund projects that have positive environmental or climate benefits. Unlike traditional bonds, green bonds are earmarked exclusively for green projects, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. By issuing green bonds, governments and corporations can raise capital to fund initiatives that contribute to a low-carbon economy while also attracting environmentally conscious investors.
India’s First Sovereign Green Bond
In early 2023, India made headlines by announcing its first sovereign green bond, marking a significant milestone in the country’s journey toward sustainable finance. This bond issuance is part of India’s commitment to meeting its climate goals and reducing its carbon footprint. With an initial issuance of around $2 billion, the government aims to channel these funds into critical green infrastructure projects, such as renewable energy and pollution control.
The launch of this bond is also symbolic of India’s increasing engagement with the global green finance community. It sends a strong message to both domestic and international investors that India is serious about addressing climate change. In a country where coal still constitutes a significant portion of the energy mix, this bond represents a step toward a cleaner energy future.
The Role of Regulatory Support
India’s green finance push is supported by favorable regulatory measures. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced guidelines for green bonds to ensure transparency and accountability. These guidelines mandate that issuers disclose the end-use of funds and periodically report on the progress of green projects funded by these bonds. SEBI’s intervention is vital in maintaining investor trust and ensuring that green bonds genuinely serve their intended purpose.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also been proactive, encouraging banks to finance sustainable projects and adopt environmentally friendly practices. Through policy measures and guidelines, RBI has been facilitating credit access for green projects, thus fostering a supportive environment for sustainable finance.
A Growing Appetite for Sustainable Investments
India’s green bond issuance has attracted considerable interest from both institutional and retail investors. With increasing awareness of climate issues, investors are looking to put their money into projects that not only yield returns but also create a positive environmental impact. This is part of a larger trend towards ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, where investors prioritize companies and projects that demonstrate a commitment to social and environmental responsibilities.
The Indian market is gradually evolving to meet this demand. Mutual funds and asset managers have started to introduce ESG-focused funds, and green bonds are an attractive addition to such portfolios. For retail investors, green bonds offer a way to align their investment choices with their values, while institutional investors see them as an opportunity to diversify portfolios while mitigating climate-related risks.

Challenges in Scaling Green Bonds
While India’s push for green bonds is promising, there are challenges that need to be addressed for sustained growth. One key issue is the need for clear and consistent reporting standards. For green bonds to be credible, it’s crucial that investors can trust that their funds are being used for genuinely green projects. However, ensuring this level of transparency can be challenging, especially given the complexities of environmental metrics and impact assessment.
Another challenge is the need for incentives. Although there is demand for green bonds, incentivizing more companies and institutions to issue these bonds can accelerate their adoption. This could be achieved through tax benefits, subsidies, or preferential interest rates for green projects.
Additionally, awareness about green bonds and sustainable finance is still limited in India. Educating investors about the benefits and impact of green bonds is essential for expanding their reach and establishing a strong market for sustainable finance.
The Future of Sustainable Finance in India
India’s push for green bonds is part of a broader vision to transform its financial ecosystem. As climate risks become more pronounced, green finance is expected to play a central role in the nation’s economic planning. The government is likely to continue exploring additional financial instruments, such as blue bonds (for ocean conservation) and social bonds (for social impact projects), to broaden the scope of sustainable finance.
In the coming years, we can also expect to see more collaboration between the public and private sectors in financing sustainable projects. The government’s focus on public-private partnerships will be crucial in mobilizing the massive funds needed for green infrastructure and climate adaptation. By working with private players, India can enhance its green financing capacity and accelerate its transition to a low-carbon economy.
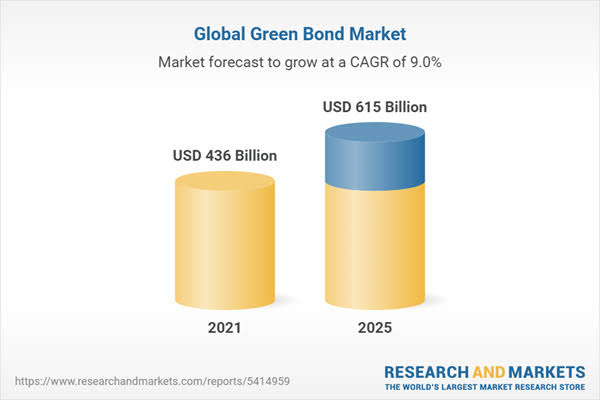
Conclusion: A Step Towards a Sustainable Future
India’s journey in the green bond market is still in its early stages, but the steps taken so far signal a strong commitment to sustainable development. The issuance of sovereign green bonds has set a precedent, and with continued regulatory support, investor interest, and public awareness, India has the potential to become a leader in green finance in Asia.
The transition to sustainable finance is not without its challenges, but the benefits are significant. By channeling investments into green projects, India can achieve both economic growth and environmental protection. The move toward green bonds is more than just a financial decision; it’s a strategic choice for the future of the nation, ensuring that growth today does not compromise the well-being of future generations. Through sustainable finance, India is taking steps to secure a healthier, more resilient, and economically inclusive future for all.
