The conflict between Ukraine and Russia is one of the most significant geopolitical crises in modern history, with implications that extend far beyond Eastern Europe. For Americans, understanding this conflict is crucial, as it impacts global security, the economy, and the future of international alliances. Here’s what you need to know about the Ukraine-Russia war and its implications for the United States and the world.
1. The Roots of the Conflict
The conflict between Ukraine and Russia is deeply rooted in history, politics, and geography. Some key aspects include:
- Historical Ties and Independence:
Ukraine was part of the Soviet Union until its dissolution in 1991, when Ukraine declared independence. Since then, Ukraine has sought to establish itself as a sovereign state while balancing its relationships with both the West and Russia. - Annexation of Crimea (2014):
In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea, a move widely condemned as a violation of international law. This marked the beginning of an armed conflict in Eastern Ukraine, with Russian-backed separatists fighting Ukrainian forces in the Donbas region. - NATO and EU Aspirations:
Ukraine’s desire to join NATO and the European Union has been a major source of tension with Russia, which views these moves as a threat to its sphere of influence.
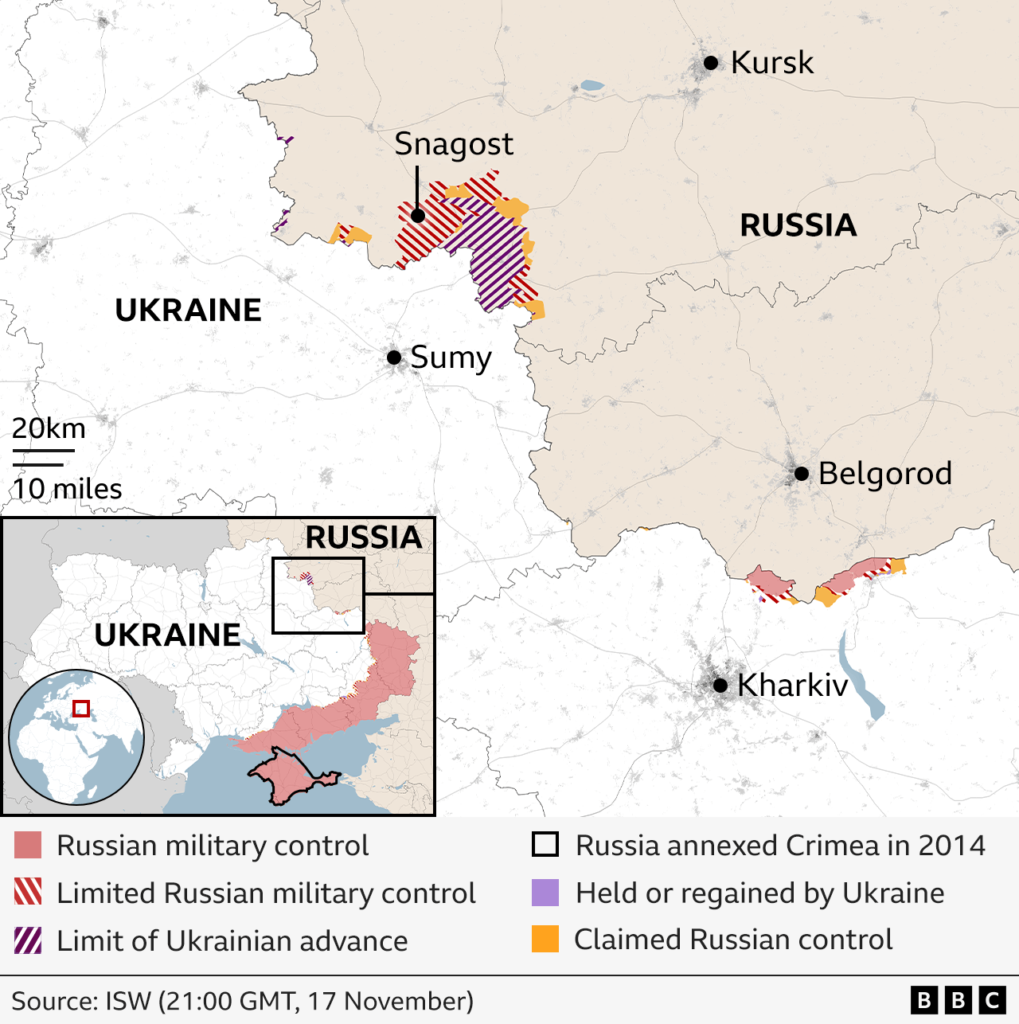
2. Why the War Began in 2022
The current war began on February 24, 2022, when Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Russian President Vladimir Putin justified the invasion with several claims, including the need to “denazify” Ukraine, protect Russian-speaking populations, and prevent NATO expansion. However, most analysts see these justifications as a pretext for Russia’s broader ambitions to reassert control over its neighbors.
3. The Humanitarian Crisis
The war has created one of the worst humanitarian crises since World War II:
- Displacement and Casualties:
Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced, with many seeking refuge in Europe and the United States. Thousands of civilians and soldiers have died, and entire cities have been reduced to rubble. - War Crimes Allegations:
Reports of atrocities, including targeted attacks on civilians, mass graves, and the use of banned weapons, have emerged, leading to accusations of war crimes against Russian forces. - Economic Devastation:
Ukraine’s economy has been severely damaged, with infrastructure, agriculture, and industries destroyed by Russian attacks.
4. Why It Matters to Americans
The Ukraine-Russia war has significant implications for the United States:
- Global Security and Democracy:
The conflict is seen as a test of the West’s commitment to defending democratic values and the sovereignty of nations. If Russia succeeds in Ukraine, it could embolden other authoritarian regimes to challenge the international order. - Energy Prices:
The war has disrupted global energy markets, leading to higher gas prices in the U.S. and Europe. Sanctions on Russian oil and gas exports have further strained supplies. - Inflation and Economic Impact:
The war has contributed to global inflation, particularly in food and energy prices. Ukraine is a major exporter of wheat and other agricultural products, and disruptions in its supply have had ripple effects worldwide. - Military Spending:
The U.S. has provided billions of dollars in military aid to Ukraine, including advanced weapons systems. While this support is essential for Ukraine’s defense, it has sparked debates about prioritizing domestic issues over foreign conflicts.
5. America’s Role in the Conflict
The U.S. has been a key player in supporting Ukraine through diplomatic, military, and economic means:
- Military Aid:
The U.S. has provided advanced weaponry, including HIMARS rocket systems, drones, and anti-aircraft missiles, to bolster Ukraine’s defenses against Russian forces. - Economic Sanctions on Russia:
Washington has imposed severe sanctions on Russia, targeting its financial institutions, energy exports, and key individuals. These sanctions aim to weaken Russia’s ability to fund the war. - NATO and Alliance Strengthening:
The conflict has revitalized NATO, with the alliance expanding its presence in Eastern Europe and welcoming new members like Finland (and potentially Sweden). This signals a renewed commitment to collective defense.
6. The Risk of Escalation
The war poses risks of escalation that could directly affect the U.S.:
- Nuclear Threats:
Russia has hinted at the potential use of nuclear weapons, raising concerns about a wider conflict. The U.S. and NATO have warned Moscow of severe consequences if it resorts to such measures. - Cyberattacks:
Russia has the capability to launch cyberattacks on U.S. infrastructure, which could disrupt critical services and further strain international relations. - Global Power Dynamics:
The war has accelerated a shift in global power dynamics, with China and Russia appearing to strengthen their alliance. This challenges the U.S.’s position as the dominant global power.
7. The Path to Peace
Ending the conflict remains a complex challenge:
- Diplomatic Efforts:
While the U.S. and its allies have called for a negotiated settlement, both Ukraine and Russia have set conditions that make peace elusive. Ukraine demands the restoration of its territorial integrity, while Russia seeks recognition of its control over annexed regions. - Rebuilding Ukraine:
Post-war reconstruction will require massive international investment. The U.S. will likely play a key role in rebuilding Ukraine’s infrastructure and economy. - Accountability:
Ensuring accountability for war crimes and violations of international law will be essential for lasting peace and justice.
Conclusion
The Ukraine-Russia conflict is more than a regional war; it’s a battle over the principles of sovereignty, democracy, and the rule of law. For Americans, the war serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of global events and the importance of standing against aggression. While the road ahead is uncertain, the United States’ role in supporting Ukraine underscores its commitment to upholding the values that define the free world.

